![]()
Intelligence Research Observatory
Research & Analysis-S.A. Cavanagh
Research Assistance-Chuck Stevens
Warfare Psychology Expert-LZ Smith MA
Methodology–Open Source Research
Cuba-The Frontline of Intelligence Warfare, an Overview
Image of Lourdes Russian Spy-Intelligence Base Cuba-Courtesy of The Diplomat

Image of Map Courtesy of FOX Carolina
Background & Analysis
- The Island of Cuba is a strategic & tactical gem for Russian and Chinese intelligence operations. Cuba is Just 94 miles from the southernmost point of the continental United States; for decades Russian military installations in Cuba have been capturing high quality SIGINT (signals intelligence), & MASINT (materials intelligence). Simultaneously Russia is exploiting US interests through offensive cyber operations. Eavesdropping US radio traffic, allowed Russia to monitor US military activities during Operation Desert Storm. Russian bases in Cuba have facilitated Russian intelligence to quietly conduct industrial espionage, stealing trade secrets from US corporations. Russia claims to have closed their military-spy bases in Cuba between 1990 and 2014; however the data dictates it is unlikely Russia completely shuttered all Spy operations. Indications Russian did not close all listening posts is demonstrated by the stay behind contingent of 3000 Russian military/civilian technicians and analysts, commanded by, high ranking officers Pavel Smolko and Alexander Utochkin, of Unit 47747 military intelligence. During this same time Russia spent $3 billion on operations and modernization of the Lourdes facility.
- De Faakto open source research & intelligence evaluation finds evidence Russia continued to operate spy and military bases, despite claims of closing & has increased intelligence gathering by partnering with Chinese intelligence units in Cuba, by training and assisting Chinese analysts, operating joint spy bases, and through joint intelligence gathering-sharing operations.
Intelligence Value-The How & Why-Key Points
- Cuba is remarkably close to the continental USA making it too strategically valuable to abandon. Cuba provides a prolific base for spying & industrial espionage, secondary benefits include the close physical observation and monitoring of US Military Base Guantanamo Bay
- Russia is either sharing or renting out their Cuban military bases and spy stations to the Chinese security apparatus. Depending on the collaboration agreement, Russia may be training and assisting Chinese intelligence analysts, for cash, Intel-espionage sharing, or operational expenses
- In the past, Russia could steal trade secrets and conduct industrial espionage activities using Cuban spy stations. China is a prolific consumer of intelligence, particularly industrial-military trade secrets for the use of counterfeiting & reverse engineering military technology. It only makes sense China would want to take over or share the intelligence infrastructure in Cuba, the benefits to both Russia and China are invaluable for intelligence gathering
- Recent re-deployment of Russian GRU scientists and mathematicians to Cuba, signals China and Russia are also collaborating on MASINT intelligence for assessing U.S. air defense system range and missile strike & targeting packages in the United States
- There is reasonable doubt; Russia’s technological capacity cannot resist Western forces alone. This is most likely why the Kremlin is working closely with Beijing, exhibiting the levels of cooperation in political intelligence sharing between the two countries
- Moscow and Beijing are believed to be already sharing large amounts of intelligence. As China gains access to the Lourdes center, that will mean more prime military intelligence products , which is important, because China is gearing up for operations against Taiwan
- Russia entered into agreements with Cuba in principal to re-establish and operate military-spy bases in 2014. This appears to have happened before Russia invaded Ukraine in 2014, this would enable, Russian spies to capture US military intelligence chatter by eavesdropping from Cuban bases. In 2017 there was more discussion about the operations in Cuba between Russian & Cuban governments. During this time Russia forgave 90% of Cuba’s unpaid Soviet-era debts, which totaled $32bn (£18.6bn) – a concession that now appears to be tied to the agreement to reopen the base.
- There has been significant investment at the Intel facility in Bejucal-Cuba. Satellite images from 2018 show a newly constructed radome on the signals intelligence base. This is a first of its kind among the numerous SIGINT antennas at Bejucal, which have been used to intercept electronic communications from the United States. The Radome, erected on a site adjacent to other known Cuban surveillance antennas south of Havana took place between 2017 and 2018. The functions of the new antenna are not discernible from the current satellite images, but similar antennas have been employed for signals interception, missile tracking, satellite uplinks and downlinks, radio communications, tracking of objects in space, and in some cases to disrupt satellite communications. The radome could also enable direct communications with vessels at sea or other signal sources on the horizon. It is notable that in 2017 Russia completed a new satellite communications ground station not far from Cuba, in Nicaragua, purportedly for GPS-type signals, indicating work towards a regional comprehensive electronic spy network.
- US intelligence sources acknowledged, China has been spying on the US from various sites based in Cuba for years, even though the White House denies reports China is building new signals intelligence facilities on the island. According to the same US intelligence sources, Chinese military and intelligence sites monitor maritime traffic, US Guantanamo naval base and communications. With so much information moving from physical lines and cables to wireless, the People’s Republic of China will move to capture more wireless data.
- It is certain, Cuban military intelligence units are partnered and working with Russia, and it is likely a new espionage partnership has been established with Chinese spies operating out of listening posts in Cuba. Information gathered by Cuban intelligence is sold to US adversaries on the market to the highest bidder, making Cuban intelligence units a freelance entity, which generates revenue for Cuba while simultaneously building alliances & allies.
End of Background & Analysis
Video Courtesy of Wall Street Journal & YouTube
The Dogs Breakfast, Everything Cuba, Military Intelligence, Espionage & Spying-Intelligence Notes, Historical Briefs and Resource Data

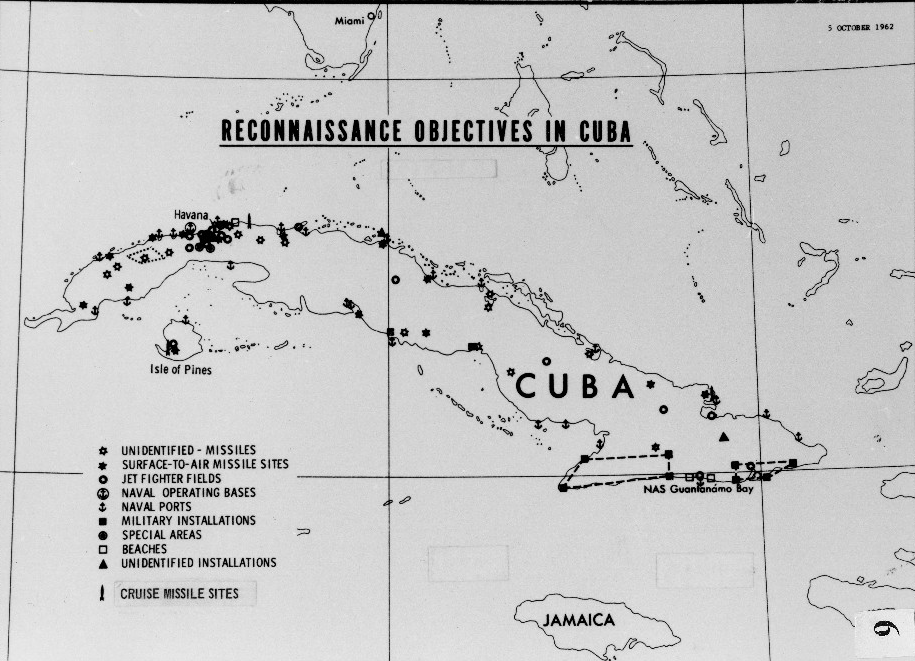
Image of Soviet 1961 Military Buildup-Courtesy of Coast Guard Aviation History & CIA
Historical Brief Cuban Missile Crisis & Bay of Pigs Invasion
In October 1962, US U-2 spy plane flights over Cuban territory revealed the missile installation sites. This discovery confronted the Kennedy Administration with its most serious foreign policy crisis.
The origins of the Cuban Missile Crisis lie in the failed Bay of Pigs invasion, during which US-supported Cuban exiles hoping to foment an uprising against Castro were overpowered by the Cuban armed forces. After the invasion, Castro turned to the Soviets for protection against future US aggression. The Soviets provided Cuba with nuclear weapons on the condition that the deal would remain secret until the missiles were fully operational. Khrushchev claimed that his motivation for providing Cuba with nuclear weaponry was to safeguard the Cuban Revolution against US aggression and to alter the global balance of power in favor of the Soviet Union. Kennedy ordered a naval “quarantine” of Cuba. The use of “quarantine” legally distinguished this action from a blockade, which assumed a state of war existed.
Kennedy sent a letter to Khrushchev declaring that the United States would not permit offensive weapons to be delivered to Cuba, and demanded that the Soviets dismantle the missile bases already under construction or completed, and return all offensive weapons to the U.S.S.R. Khrushchev sent another message indicating that any proposed deal must include the removal of U.S. Jupiter missiles from Turkey. That same day a U.S. U–2 reconnaissance jet was shot down over Cuba. Kennedy and his advisors prepared for an attack on Cuba within days as they searched for any remaining diplomatic resolution. Kennedy set forth in his message to the Soviet leader proposed steps for the removal of Soviet missiles from Cuba under supervision of the United Nations, and a guarantee that the United States would not attack Cuba. In return the US would remove Jupiter missiles from Turkey (US Government Office of the Historian, 1962)
Video Courtesy of Hindustan Times
Havana Syndrome
In 2016, United States diplomats in Havana began to report unusual sensory and auditory stimuli, as well as dizziness, tinnitus, and other cognitive manifestations. A 6-7 month follow-up revealed persistent abnormalities in the cognitive, vestibular, and oculomotor domains. The variety of presenting symptoms made diagnosis difficult, so many theorised about the origin of the injury. Later, the Canadian diplomats and their families stationed in Havana described a similar set of symptoms
Mechanism of injury
- The primary cause of these changes is unknown, and unravelling this mystery will necessitate additional research into the association between neural effects and symptoms. However, one study suggested that these symptoms were caused by acquired neurotoxicity. As a result, overexposure to cholinesterase inhibitors is hypothesized to be a possible cause. Also, using a pulsed microwave may be a possible culprit
Clinical Presentation
- There are acute and chronic symptoms of Havana Syndrome (HS).
Acute symptoms
- sudden onset of a perceived loud noise (screeching, chirping, clicking, or piercing).
- visual disturbances (blurred vision and sensitivity to light).
- sensation of intense pressure or vibration in the head
- pain in the ear or more diffusely in the head
- tinnitus and hearing loss
- dizziness, unsteady gait
Chronic symptoms
- Insomnia
- Dizziness and nausea
- Light sensitivity and eye strain
- Sound sensitivity
- Tinnitus and hearing reduction
- Impaired concentration and memory
- Irritability, nervousness, and sadness
- Fatigue
- Headache
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) findings
- Both US and Canadian participants had neuroimaging abnormalities associated with their existence in Havana. In the United States, researchers discovered variances in grey and white matter (WM) volume, cerebellar diffusion properties, and functional network connectivity
- The findings show a decrease in white matter fibre density and network structural connectivity in Canadians who spent more than a month in Havana between 2016 and 2018. Microstructural changes in the fornix (a triangular area of white matter in the mammalian brain between the hippocampus and the hypothalamus) were discovered using advanced diffusion-weighted imaging techniques (diffusion magenetic resonance imaging), which corresponded to headaches and tinnitus. There are also microstructural changes in the splenium (the thick posterior part of the corpus callosum of the brain), which have been linked to headaches and fatigue. Furthermore, there is evidence of disrupted structural network connectivity in commissural thalamic and hippocampal projections to the brain’s posterior regions. The precise reason for the observed white matter differences is unknown.
Management
- Acute Treatment: There is no documented therapeutic option for the acute symptoms of this disorder. Overall, patients are given rest and instructions to mitigate the circumstances that caused the initial signs and symptoms. Patients should be eliminated from the initial site and transferred to a secure site as promptly as possible
- Chronic Treatment: There is no established therapeutic option for this syndrome’s chronic symptoms. In general, patients with chronic conditions are treated with interdisciplinary rehabilitation (Physiopedia, 2024)

Image of Reactivated Russian Radar Site Courtesy of The Aviationist
Does Russia Have Military Installations in Cuba?
- The Soviet Union previously had a sizeable military presence in Cuba, which for much of the Cold War was the early country in the Western Hemisphere outside the western sphere of influence. Russia closed its military facilities in Cuba, shortly after the Soviet collapse, but has recently sought to expand its military presence outside the former Soviet Union with new bases. The possibility of re-establishing bases in Cuba was previously raised in 2017. In Cuba surveillance facilities of unknown origin have been speculated to be either Russian or Chinese, and the possibility of a restoration of Russian facilities in the country has been raised multiple times (Military Watch Magazine, 2022)
2014-Cuba Reaches Principled Agreement to Allow Russia to Establish New Spy Bases for Cash
- Russia has quietly reached an agreement with Cuba to reopen a Soviet-era spy base on America’s doorstep, amid souring relations between Moscow and Washington
- The deal to reopen the signals intelligence facility in Lourdes, south of Havana, was agreed in principle during President Vladimir Putin’s visit to the island in 2014, according to the newspaper Kommersant
- Opened in 1967, the Lourdes facility was the Soviet Union’s largest foreign base, a mere 155 miles from the US coast. It employed up to 3,000 military and intelligence personnel to intercept a wide array of American telephone and radio communications, but Putin announced its closure in 2001 because it was too expensive – Russia had been paying $200m (£117m) a year in rent – and in response to US demands
- After Putin visited Cuba, the Kremlin press service said the president had forgiven 90% of Cuba’s unpaid Soviet-era debts, which totalled $32bn (£18.6bn) – a concession that now appears to be tied to the agreement to reopen the base
- “Lourdes gave the Soviet Union eyes in the whole of the western hemisphere … For Russia, which is fighting for its lawful rights and place in the international community, it would be no less valuable than for the USSR,” Vyacheslav Trubnikov, former head of Russia’s foreign intelligence service told Kommersant (Guardian, 2014)
- The move appears to be part of Moscow’s campaign to reassert itself as a geopolitical rival to the United States and comes as the west is set to expand sanctions against Russia over its role in the Ukraine conflict
- Cuba SIGINT Less About Spying and More about Stealing Commercial-Industrial Secrets-Some Disagree
- Moscow-based defence analyst Pavel Felgenhauer called the reported re-establishment of the Lourdes base, to show Washington the “middle finger” and said it was prompted in part by the expansion of western influence in Ukraine
- “There’s not much radio chat left of any importance, it’s all going to coded channels, so I think the intel-gathering value would be much less than 20 years ago,” he said. However, the base could be useful for stealing commercial secrets, Felgenhauer admitted, “because when individuals chatter they’re not always so attentive of secure lines”
- But Ruslan Pukhov, the director of the Centre for the Analysis of Strategies and Technologies in Moscow, said the base does have military value and that negotiations with Cuba were likely mostly completed before the Ukraine crisis even started in November. The reopening follows Russia’s attempts to break its “strategic solitude” by improving military cooperation with other countries and said it could share information from the base with US rivals like China, he said (Guardian, 2014)
Here’s what a Congressional report from 2000 said about the facility in Lourdes Cuba
- In 2000 the Secretary of Defense formally expressed concerns to Congress regarding the espionage complex at Lourdes, Cuba, and its use as a base for intelligence directed against the United States
- The Secretary of Defense, referring to a 1998 Defense Intelligence Agency assessment, reported that the Russian Federation leased the Lourdes facility for an estimated $100 million to $300 million a year
- It has been reported that the Lourdes facility was the largest such complex operated by the Russian Federation and its intelligence service outside the region of the former Soviet Union
- The Lourdes facility was reported to cover a 28 square-mile area with over 1,500 Russian engineers, technicians, and military personnel working at the base
- Experts familiar with the Lourdes facility have reportedly confirmed that the base had multiple groups of tracking dishes and its own satellite system, with some groups used to intercept telephone calls, faxes, and computer communications, in general, and with other groups used to cover targeted telephones and devices
- News sources have reported that the Lourdes facility obtained sensitive information about United States military operations during Operation Desert Storm
- Academic studies cite official U.S. sources affirming that the Lourdes facility was used to collect personal information about United States citizens in the private and government sectors, and offered the means to engage in cyber warfare against the U.S.
- The operational significance of the Lourdes facility reportedly grew dramatically after Russian President Boris Yeltsin issued a 1996 order demanding the Russian intelligence community increase its gathering of U.S. and other Western economic and trade secrets
- It has been reported that the Government of the Russian Federation is estimated to have spent in excess of $3 billion in the operation and modernization of the Lourdes facility
- Former U.S. Government officials were quoted confirming reports about the Russian Federation’s expansion and upgrade of the Lourdes facility
- It was reported in December 1999 that a high-ranking Russian military delegation headed by Deputy Chief of the General Staff Colonel-General Valentin Korabelnikov visited Cuba to discuss the continuing Russian operation of the Lourdes facility
- Defense experts agree the base could significantly boost Russia’s ability to spy on America during a low-point in U.S.-Russia relations
- Ivan Konovalov, head of the Moscow-based Center for Strategic Trends Studies, estimated that the Lourdes base was used to acquire at least 50% of the Soviet Union’s radio-intercepted intelligence from the U.S., according to Reuters
- Reopening the Lourdes base could boost Russia’s intelligence-gathering capabilities “quite significantly” as U.S.-Russia relations remain strained. “One needs to remember that Russia’s technical intelligence abilities are very weak. This will help,” Konovalov told Reuters.
- If reopened, the base will demonstrate Russia’s interest in maintaining its own alliances to counter those of the U.S. (Business Insider, 2014)
Video Courtesy of FOX Carolina
2023 Chinese Military-Spy Apparatus moves into Russian bases in Cuba
China Takes over Some Former Soviet Spy Bases, Russia Partners with China, & never Actually Stops Spying from Cuba
- Moscow is more likely to join efforts with Cuba-based Chinese SIGINT facility, targeting the U.S. The RLI predicted in February 2022 that Russia might reopen the Lourdes intelligence facility that had been closed since 2001
- The forecast is confirmed by the fact that the center has resumed its activity. Some GRU agents with the 6th Radio Intelligence Directorate are reported to arrive in Cuba as diplomats, missile engineers, computer technology and exact mathematics experts. With the center officially closed by the Russians, some employees stayed in Cuba, including Pavel Smolko and Alexander Utochkin, officers of 47747 military units (in Klimovsk, where equipment from Lourdes was transported)
- With experts of that kind, the Lourdes center will most likely collect not just SIGINT but also MASINT, which means assessing U.S. air defense systems range and developing routes for possible missile strikes targeting the United States
- These assessments are based on studying the experience of Russian military intelligence before and after a full-scale invasion of Ukraine. Russian diplomats in Europe, especially missile engineers, are also known to carry out these functions
- Lourdes Radio Electronics Center (REC), not far from Havana, is able to grab traffic carried by American communications satellites, eavesdrop on telephone communications and intercept messages from the NASA Mission Control Center in Florida
- China has reached a secret deal with Cuba to establish an electronic eavesdropping facility on the island roughly 100 miles (160 km) from Florida, the Wall Street Journal said. But Cuban vice Foreign Minister Carlos Fernandez de Cossio denied the agreement
- The tasks listed for the facility correspond to the capacity of the Lourdes center. The data that requires additional verification suggest that some premises were leased to China after the center had been closed in 2001, which means the Chinese have long been present there. China’s paramount Xi Jinping visited Cuba in 2014 with the Chinese president engaging in a follow-up visit with Cuba’s dictator, Raul Castro, in 2016. China reactivated Lourdes as well as three other intelligence stations on Cuba in 2019.
- There are reasonable doubts that Russia’s technological capacity is able to ensure the work of the center at present, as Russia is not able to successfully resist the West on its own. That is why the Kremlin counts on Beijing. Russia and China will possibly share the Lourdes center. That is in line with the level of cooperation in political intelligence sharing between the two countries. Russian foreign intelligence chief Naryshkin acknowledged on January 17, 2023, that Moscow and Beijing are sharing a large amount of intelligence, operational and signal data. If China gains access to the Lourdes center, that will mean more military intelligence sharing. We believe this prospect has a high chance, as China is gearing up for an operation against Taiwan, potentially triggering a conflict with the United States. (Lansing Institute 2023)


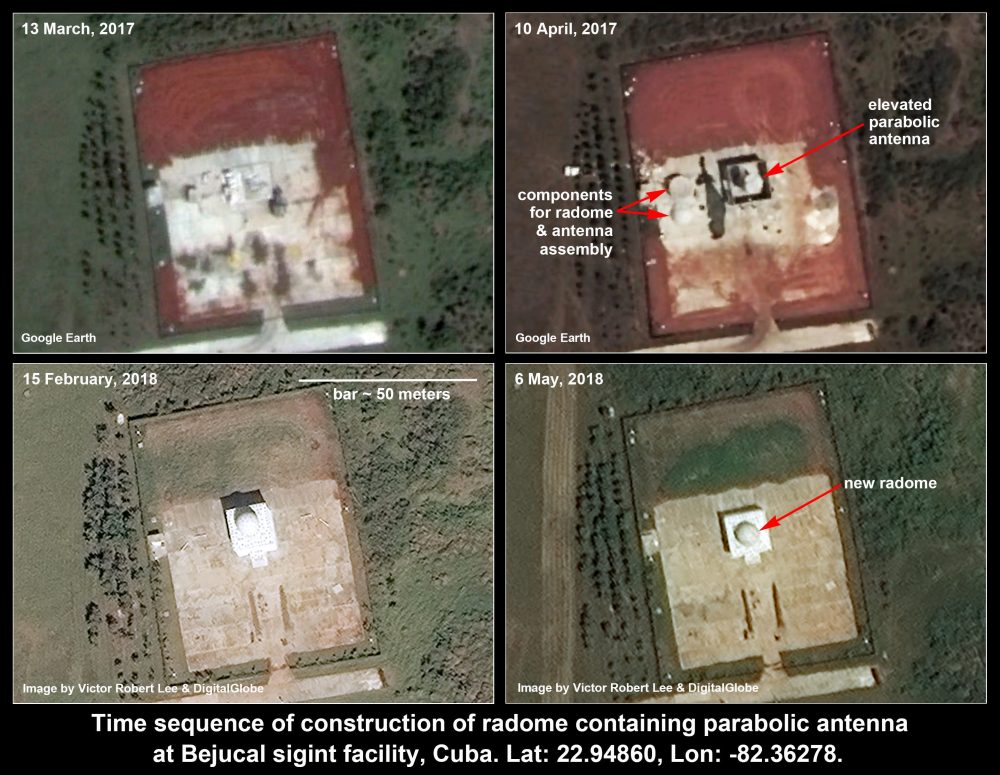
Significant Investment-New SIGINT Radome at Intel Base in Bejucal-Cuba
- Satellite images from February and May 2018 show a newly constructed radome on the signals intelligence base near Bejucal, Cuba
- Its protective dome and elevated mounting make it the first of its kind among the numerous long-standing sigint antennas at Bejucal, which have been used to intercept electronic communications from the United States
- The new steerable parabolic antenna and its spherical enclosure (together called a radome) were erected on a site adjacent to other known Cuban surveillance antennas south of Havana near the town of Bejucal between March 2017 and February 2018
- The functions of the new antenna are not discernible from the current satellite images, but similar antennas have been employed for signals interception, missile tracking, satellite uplinks and downlinks, radio communications, tracking of objects in space, and in some cases to disrupt satellite communications
- The radome, approximately 6-7 meters in diameter, sits atop a square building approximately 11-12 meters wide. If the antenna can be tilted to horizontal – a common capability – its elevated position could also enable direct communications with vessels at sea or other signal sources on the horizon
- The Bejucal signals intelligence site had a relatively static number of parabolic antennae, the new radome, was covered, although such coverings are common in many other nations, particularly at facilities with military or intelligence functions. Such specialized coverings can protect from weather and wear, but another advantage is that they conceal the orientation, and thus the possible purposes, of the antenna within
- Satellite images of the signals intelligence base near Bejucal also show that two smaller steerable parabolic antennas were installed in April-May 2017, the same period as the beginning of construction of the new radome. These antennas, located 460 meters south of the newly constructed radome, are linked by above-ground conduits to two other antennas installed as recently as May 2016
- The difference in size and architecture of the new radome antenna structure compared to the stand-alone parabolic dish installations present over the past ten years at Bejucal indicates a new level of investment in such facilities; the source of this investment is not clear
- The governments of both Russia and China have recently signalled their intent to augment military and economic investments in Cuba. In 2014, Russian President Vladimir Putin wrote off approximately 90 percent of the $32 billion Cuba owed on Soviet-era debt
- Russia shut down Lourdes in 2001. In 2016 a senior Russian defense official suggested Russia was considering reopening a military base in Cuba. The Russian signals intelligence ship Viktor Leonov docked at the port of Havana in 2014, 2015, 2017, and most recently in March 2018, following a reconnaissance patrol along the southeast coast of the U.S. that included an excursion within 20 nautical miles of the Kings Bay submarine base in Georgia. In 2017 Russia completed a new satellite communications ground station not far from Cuba, in Nicaragua, purportedly for GPS-type signals, but other uses cannot be ruled out
- Cuba’s largest international creditor and trading partner is China, which recently made a $120 million development loan for a container port at Santiago de Cuba. In the past three years, several Chinese companies have announced investments in Cuba. Visits by high-level Cuban and Chinese military leaders took place in 2015-2017
- There is scant public evidence that Beijing is behind the new radome at Bejucal, but the US Senate’s Committee on Foreign Relations as well as the Select Committee on Intelligence, identified China in 2016 as being active in Cuba-based electronic surveillance of the U.S. by referring publicly to “this Chinese listening station in Bejucal”
- China has also recently built a space tracking station in Argentina, operated by China’s military, that experts say could have both civilian and military/intelligence purposes, and which has a longitudinal alignment with geosynchronous satellites stationed above the U.S. Eastern Seaboard that control civilian and defense communications (The Diplomat, 2016)
Cuba Selling SIGINT-Freelancing Intercepts to 3rd party Buyers
The Cuban government has been reported to sell its intercept data from U.S. communications to third-party buyers, particularly military adversaries of the U.S. Also, in 2003, Persian-language satellite transmissions by Voice of America and the Los Angeles-based Iranian opposition television network NITV were reported to have been blocked by jamming signals originating from Cuba
The brand new installation at the Bejucal base suggests augmented capabilities for signals interception and disruption by Cuba, China, Russia, or a combination of these authoritarian governments, via a facility less than 550 kilometres from U.S. Central Command, and ideally situated to intercept signals from geosynchronous satellites servicing the entire Eastern United States (The Diplomat, 2018)
Russian Military Installations in Cuba
- Holguin
- Remedios
- Artemisia
- Santiago de las vegas (CIA Reading Room, Declassified 2004)
What is the Purpose of the USA Naval Base Guantanamo, Cuba?
Mission-Guantanamo
- Judging by its location, Guantanamo Bay has more than just one mission. When it comes to its location, it is excellent for the ships that require refuelling operations. Other than that, the international channel for shipping in the area must be constantly maintained, not to mention about the proximity to the Caribbean. The installation is part of a treaty with Cuba, so even if all these things would be useless, it would still have to be there
- As for the logistic support and operations, the facility is an essential “tool” in the fight against the drug traffic from the Caribbean to the United States of America. The experts on site provide logistic help to all the troops struggling to eliminate the traffic. Most of the operations in the Caribbean – regardless of their nature – come and connect to this base
- One of the aspects that tensioned the relations between the United States of America and Cuba is the migrant history. The USA aims to eliminate the communist regime and supports the migrants, but it also disagrees with the idea of illegal migrants. Therefore, Guantanamo Bay has something to do in this process too. It helps the migrants accommodate in their attempt to escape from the communist country (Military Bases.Com, ND)
How did the USA get a Military Base in Cuba?
- The story of Guantanamo goes back more than a century, to the time of the Spanish-American War
- Until 1898, Cuba had belonged to Spain; as the Spanish empire diminished, Cubans fought for their independence. The U.S. joined in to help its neighbours and, though the Spanish-American War ended up focused mainly on the Spanish presence in the Philippines, Cuba was the site of the sinking of the USS Maine, the event that precipitated American military involvement. When the war ended, Spain gave the U.S. control of Cuba — among other territories, like Puerto Rico — three years later, Cuba became an independent nation
- However, that independence was not without a catch: as part of the Platt Amendment, the document that governed the end of the occupation, the new Cuban government was required to lease or sell certain territory to the United States
TIME Magazine Historical Summary of Events- Guantanamo Bay Naval Base
- In 1934, the U.S. recognized Cuba’s “ultimate sovereignty” over the 45-sq.-mi. enclave in Oriente province near the island’s southeast end. In return, Cuba yielded the U.S. “complete jurisdiction and control” through a perpetual lease that can be voided only by mutual agreement.
- For a low rental ($3,386.25 annually), the U.S. Navy gets its best natural harbour south of Charleston, S.C., plus 19,621 acres of land, enough for a complex of 1,400 buildings and two airfields, one of them capable of handling entire squadrons of the Navy’s fast jets. In terms of global strategy, Guantanamo has only marginal value. It served as an antisubmarine center in World War II, and could be one again. But its greatest worth is as an isolated, warm-water training base for the fleet. With an anchorage capable of handling 50 warships at once, it is the Navy’s top base for shakedown cruises and refresher training for both sailors and airmen. What Cuba gets out of the deal is 3,700 jobs for the technicians and labourers who help maintain the base, a payroll of $7,000,000 annually (Time Magazine, 2015)
GITMO Detention Facility
Guantánamo Bay detention camp, U.S. detention facility on the Guantánamo Bay Naval Base, located on the coast of Guantánamo Bay in south-eastern Cuba
- Constructed in stages starting in 2002, the Guantánamo Bay detention camp (often called Gitmo, which is also a name for the naval base) was used to house Muslim militants and suspected terrorists captured by U.S. forces in Afghanistan, Iraq, and elsewhere (see also Iraq War). The facility became the focus of worldwide controversy over alleged violations of the legal rights of detainees under the Geneva Conventions and accusations of torture or abusive treatment of detainees by U.S. authorities
- In early 2002 the camp began receiving suspected members of al-Qaeda, the terrorist organization responsible for the September 11, 2001, attacks, and fighters for the Taliban, the Islamic fundamentalist faction that had ruled Afghanistan (1996–2001) and harbored al-Qaeda leader Osama bin Laden and his followers. Eventually hundreds of prisoners from several countries were held at the camp without charge and without the legal means to challenge their detentions. The administration of Republican Pres. George W. Bush maintained that it was neither obliged to grant basic constitutional protections to the prisoners, since the base was outside U.S. territory, nor required to observe the Geneva Conventions regarding the treatment of prisoners of war and civilians during wartime, as the conventions did not apply to “unlawful enemy combatants”
- Several prisoners who had been cleared for release in other countries or for transfer to their home countries continued to be detained, either because no country would accept them or because their home countries were deemed too volatile to guarantee their secure imprisonment
- The camp was repeatedly condemned by international human rights and humanitarian organizations—including Amnesty International, Human Rights Watch, and the International Committee of the Red Cross—as well as by the European Union and the Organization of American States (OAS), for alleged human rights violations, including the use of various forms of torture during interrogations. In response to such criticism, the Bush administration generally insisted that detainees were well cared for and that none of the “enhanced interrogation techniques” employed on some prisoners were torturous
- Additionally, according to U.S. officials, the use of such techniques had in many cases—e.g., in the interrogation of Khalid Sheikh Muhammad, the alleged mastermind of the September 11 plot—yielded valuable intelligence on the leadership, methods, and plans of al-Qaeda and other terrorist organizations. (Britannica, 2024)
- It has been 22 years since the U.S. opened a military prison in Guantanamo Bay, Cuba, to hold suspected terrorists after the 9/11 attacks. That prison remains open today. It still holds 30 men, many of whom have never been criminally charged. The prison will remain open for the foreseeable future as no administration has been able to close the facility as the State Department couldn’t find a single country in the world willing to receive some of these cleared-for-release men. (NPR, 2024) The detention facility at GITMO is the longest standing military detention camp in history.
US Fears Chinese Troops Garrison in Cuba
- China and Cuba are negotiating to establish a new joint military training facility on the island, sparking alarm in the U.S. that it could lead to the stationing of Chinese troops and other security operations just 100 miles off Florida’s coast, the Wall Street Journal reported on Tuesday citing current and former U.S officials (Reuters, 2023)
China has been operating a spy base in Cuba since at least 2019,
- This is part of a global effort by Beijing to upgrade its intelligence-gathering capabilities, according to a Biden administration official
- The official, who was not authorized to comment publicly and spoke on the condition of anonymity, said the U.S. intelligence community has been aware of China’s spying from Cuba and a larger effort to set up intelligence-gathering operations around the globe for some time
- The Biden administration has stepped up efforts to thwart the Chinese push to expand its spying operations and believes it has made some progress through diplomacy and other unspecified action, according to the official, who was familiar with U.S. intelligence on the matter
- The existence of the Chinese spy base was confirmed after The Wall Street Journal reported on Thursday that China and Cuba had reached an agreement in principle to build an electronic eavesdropping station on the island. The Journal reported China planned to pay a cash-strapped Cuba billions of dollars as part of the negotiations (AP News, 2024) (CNN, 2023)

![]()
Resources
US confirms China has had a spy base in Cuba since at least 2019-AP World- AAMER MADHANI (2024) https://apnews.com/article/china-cuba-spy-base-us-intelligence-0f655b577ae4141bdbeabc35d628b18f
China plans a new military training facility in Cuba, Wall Street Journal reports-Reuters-Reuters-Reporting by Jose Joseph in Bengaluru; Editing by Muralikumar Anantharaman (2024) https://www.reuters.com/world/china-plans-new-military-training-facility-cuba-wsj-2023-06-20/
China has been operating military and spy facilities in Cuba for years, US officials say-CNN-Alex Marquardt, Jasmine Wright and Zachary Cohen (2023) https://www.cnn.com/2023/06/10/politics/china-military-spy-facilities-cuba-us/index.html
Guantánamo Bay has been open for 22 years despite calls for its closure-NPR- Sacha Pfeiffer, Christopher Intagliata, Gus Contreras, Emma Klein (2024) https://www.npr.org/2024/01/09/1223788648/guantanamo-bay-has-been-open-for-22-years-despite-calls-for-its-closure
Guantánamo Bay detention camp, United States detention facility Cuba-Britannica-Jeanette Nolan (2024) https://www.britannica.com/topic/Guantanamo-Bay-detention-camp
Guantanamo Naval Base in Guantanamo, CUBA-MilitaryBases.com-Staff (ND) https://militarybases.com/overseas/cuba/guantanamo-bay/
Why the United States Controls Guantanamo Bay-TIME-LILY ROTHMAN (2015) https://time.com/3672066/guantanamo-bay-history/
CIA Reading Room (2024) https://www.cia.gov/readingroom/docs/CIA-RDP65B00383R000100250078-1.pdf
Satellite Images: A (Worrying) Cuban Mystery The new radome in Cuba is unprecedented. Who is behind it? The Diplomat- Victor Robert Lee (2018) https://thediplomat.com/2018/06/satellite-images-a-worrying-cuban-mystery/
China Builds Space-Monitoring Base in the Americas- The Diplomat- Victor Robert Lee (2016) https://thediplomat.com/2016/05/china-builds-space-monitoring-base-in-the-americas/
China likely to share SIGINT with Russians-The Lansing Institute-Staff Analysts (2023) https://lansinginstitute.org/2023/06/27/china-likely-to-share-sigint-with-russians/
Everything We Know About The Huge Spy Base In Cuba That Russia Is Reopening-Business Insider-Corey Adwar and Michael B Kelley (2024) https://www.businessinsider.com/the-spy-base-russia-may-reopen-in-lourdes-cuba-2014-7
Russia to reopen spy base in Cuba as relations with US continue to sour-The Guardian- Alec Luhn (2014) https://www.theguardian.com/world/2014/jul/16/russia-reopening-spy-base-cuba-us-relations-sour
The Cuban Missile Crisis, October 1962-Office of the Historian (2024) https://history.state.gov/milestones/1961-1968/cuban-missile-crisis
Russia Threatens Opening Bases in Venezuela and Cuba as NATO Considers Ukraine’s Entry-Military Watch Magazine-Editorial Staff (2022) https://militarywatchmagazine.com/article/russia-bases-venezuela-cuba-nato
Havana Syndrome-Physiopedia-Staff Writers (2024) https://www.physio-pedia.com/Havana_Syndrome