DE FAAKTO INTELLIGENCE RESEARCH OBSERVATORY
ALTERING THE BALANCE OF POWER-CONTROL OF LUNAR RESOURCES AND CISLUNAR SPACE-AN OPEN SOURCE INTELLIGENCE STUDY
METHODOLOGY-OSINT research
BACKGROUND & ANALYSIS
Establishing a strategic presence on the Moon and in Cislunar space will alter the balance of power on Earth. The military will be particularly interested in Cislunar space as it is traditionally responsible for the protection of trade routes and lines of communication. Who ever controls Cislunar space will have a position of advantage & superiority “The High Ground” -a positional and logistic advantage from which it could occupy, constrict, threaten or coerce other space nation’s interests. (Space.com, 2019) The discovery of water and resources on the moon has changed the strategic value of Cislunar space. With the availability of lunar water, fuel can be manufactured on the moon closer to its point of use. This will allow satellites and spacecraft to be refuelled in space, which will reduce the prohibitive fuel payloads required for many space missions. Satellites can be refuelled in geosynchronous orbit. Space missions to the Moon and Mars will no longer need to carry massive amounts of fuel, as they can be refuelled in flight. Fuel will be more readily available for moon based activities, lunar mining, and harvesting minerals from passing asteroids. Satellites will have improved refuelling logistics for more remote positioning; this will provide enhanced satellite capability for space agencies, civilian commerce and military applications in Cislunar Space. The most concentrated deposits of lunar water are locked in ice at the South Pole of the Moon. Metals, aggregates, glass and ceramics can be extracted from moon rocks and soil to manufacture space faring materials. Space treaties prohibit ownership of Lunar territory and resources. The nation or agency that establishes a base closest to the resource can harvest it for use. NASA, for example has a declared a buffer zone at the Apollo landing sites for historical reasons. Similar industrial or scientific buffer applications could be declared for harvesting Lunar resources. With the inevitable & unrestricted militarization of space on the horizon, the strategic value of Cislunar and Moon based presence can not be underestimated by space faring nations.
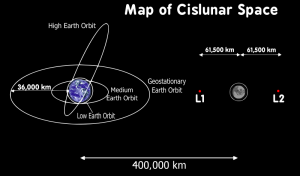
[Diagram-Cislunar Space-wpclipart, 2019]
Key Points
Cislunar Space, What is it?
- Cislunar Space is the region beyond the earth’s atmosphere occurring between the earth and moon (Collins, 2019)
- Some Cislunar Space definitions include the Lagrange Points
Lagrange Points, What are they?
- Lagrange Points are positions in space where the gravitational forces of a two body system like the Sun and the Earth produce enhanced regions of attraction and repulsion
- These can be used by spacecraft to reduce fuel consumption needed to remain in position (NASA Science, 2018)
Lunar Water
- There is frozen water on the moon
- The most concentrated deposits of lunar ice are located within craters at the South Pole of the moon (National Interest, 2019)
- There are some smaller scattered deposits of lunar ice located near the Northern Pole of the moon
Why Does Lunar Water Matter?
- Heavy fuel loads on spacecraft are prohibitive to many space missions
- For example, Apollo missions required a massive rocket, weighing about 6,500,000 pounds at launch (Space.com, 2019)
- Exploiting water from the surface of the moon will allow space industries to manufacture fuel at the moon
- Manufacturing fuel at the moon allows spacecraft to be refuelled in space closer to the destination or mission
- Satellites can be refuelled in low, medium or geosynchronous earth orbits
- Spacecraft travelling to the Moon or Mars can be refuelled in flight
- Spacecraft performing other activities such as asteroid mining can be refuelled in space (National Interest, 2019)
Who Gets to Harvest Lunar Water?
- Ownership of lunar water and other moon resources is prohibited by space treaties
- However lunar water can be harvested for use (National Interest, 2019)
- A nation present on the moons surface can hypothetically declare a safety zone for scientific instrumentation and infrastructure
- Strategic presence will allow use of near by resources
- Whoever gets to the craters at the South Pole first, and establishes a strategic presence on the moon before other nations will be able harvest lunar water (Space.com, 2019)

What Other Resources are There on the Moon?
The Moon offers other material and energy resources needed to create new space faring capability,
- Regolith aggregate
- Glass and ceramics can be made from lunar soil
- Metals can be extracted from lunar rocks and used for solar cell fabrication
- Technology already exists for these applications (Air&Space.com, 2019)
Lunar Territorial Claims
- No nation can own the moon, according to the 1967 Outer Space Treaty
- Because there are no territorial ownership rights on the moon, there fore being present in an area assures possession
- For example-NASA has declared a buffer zone of 1.2 miles to protect the Apollo landing sites historical significance (National Interest, 2019)
Control of Cislunar Space
- Cislunar space is strategically vital because the exploitation of space resources can — and will — alter the balance of power on Earth
- Cislunar space offers a vast military manoeuvre space that is difficult to surveil and from which surprises can then emerge, analogous to deep-sea submarine warfare (Space.com, 2019)
Cislunar Space is the high ground
- Who ever controls cislunar space will have a position of advantage & superiority “The High Ground” -a positional and logistic advantage from which it could occupy, constrict, threaten or coerce other space nation’s interests
- The military will be interested in the high ground of cislunar space as it is traditionally responsible for the protection of trade routes and lines of communication
- The space nation that maintains a presence in and around cislunar space will have the leverage to protect its own satellites and those of allies
- A space agency, building a cislunar space faring transportation system would put it in a position to dispatch spacecraft to any point in the Earth-Moon neighbourhood, whether for science, commerce, or defense (Space.com, 2019)
What is the Value of Cislunar Space Control?
China has Demonstrated the Value of Cislunar Space Control
- In 2010 China flew the Chang’E-2 scientific spacecraft to the Moon, orbited it for a year, then moved the spacecraft to a halo orbit around the Earth-Moon L-2 libration point (60,000 km above the center of the lunar far side)
- After loitering there for eight months, Chang’E-2 then took off for a flyby interception of the asteroid Toutati
- In a single mission, China demonstrated “space control,” or the ability to place any kind of satellite—friendly or unfriendly—virtually anywhere in cislunar space (Air&Space.com, 2011)
What are Chinas Intentions in Cislunar Space?
- China is absolutely clear on its strategic intent in cislunar space
- China intends to build an infrastructure to industrialize the moon, and use its resources and ideal location to build large numbers of solar-power satellites for their own energy supply and service a $20 trillion energy market (Space.com, 2019)
- China recently landed a lunar probe on the Moon’s far side. This is technically difficult because it is out of sight of the earth and requires a series of support spacecraft to relay data. Landings like this show China’s readiness to land on South Pole crater tops (National Interest, 2019)
Resources
US Military Eyes Strategic Value of Earth-Moon Space-Leonard David-Space.com (2019) https://www.space.com/us-military-strategic-value-earth-moon-space.html
Definition of ‘cislunar space’-Collins English Dictionary (2019) https://www.collinsdictionary.com/dictionary/english/cislunar-space
What is a Lagrange Point? NASA Science (2018) https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/resources/754/what-is-a-lagrange-point/
Diagram-Cislunar Space-wpclipart (2019) https://www.wpclipart.com/space/diagrams/Cislunar_space.png.html
Why America Needs a Presence on the Moon-Harry Foster-The National Interest (2019) https://nationalinterest.org/blog/buzz/why-america-needs-presence-moon-42507
A Rationale for Cislunar Space-Paul D. Spudis-Air & Space (2011) https://www.airspacemag.com/daily-planet/a-rationale-for-cislunar-space-168379297/
The Moon’s Role in the New U.S. Space Force- Paul D. Spudis-Air & Space (2018) https://www.airspacemag.com/daily-planet/moons-role-new-us-space-force-180970056/